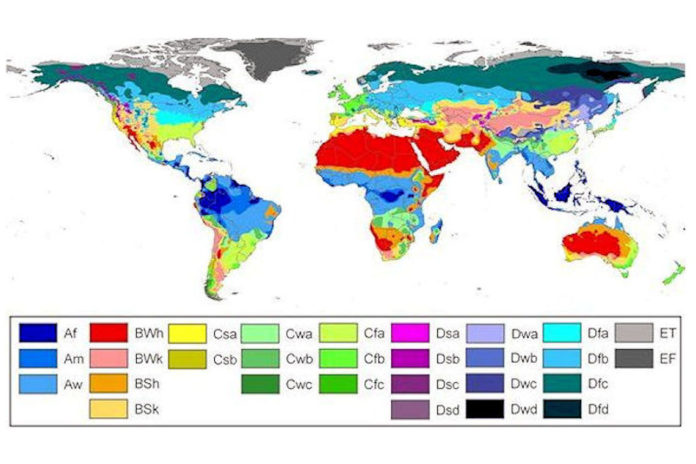
Climate classification is explored. Climate refers to the weather conditions in an area over the period a year. On the other hand, weather refers to the atmospheric conditions at one moment in time.
To study the atmospheric conditions of the world, the climate is classified into different types. The classification of the world’s climates is based on air temperature and rainfall. Koppen’s system is the most popular method for classifying the earth’s climates.
The Major Climate Types
Tropical (A) Climates
The tropical climates are found in areas near the equator. They are typically regions with high temperatures throughout the year. There are two major A climates:
Af (tropical rainforest): This tropical climate has high temperatures and high rainfall throughout the year.
Aw (tropical savannah): The savannah climate has high temperatures year round. However, it has a seasonal (wet season and dry season) rainfall pattern.
Arid (B) Climates
Arid climates are found in subtropical areas. The subtropics lie just north and south of the equator (about 30° latitude). Arid climates are regions with low precipitation (rainfall) throughout the year. There are two major B climate types:
BW (arid desert): The desert climate may have hot or cold temperatures throughout the year. However, it has consistently low rainfall throughout the year.
BS (semi-arid steppe): The BS climate may have hot or cold temperatures over the year. However, it has semi-arid (very low rainfall) conditions throughout the year
Temperate (C) Climates
These climates are usually found in midlatitude areas (about 60° latitude). They are also located near coastal areas. These areas have more moderate temperatures year round because of the ocean’s influence.
Cf (Marine west coast): This climate has moderate temperatures year round. It also has rainfall throughout the year.
Cs (Mediterranean): Mediterranean climates have moderate temperatures year round. However, it has a seasonal (wet and dry) rainfall pattern.
Cold (D) Climates
The D climates are also found in midlatitude areas (about 60° latitude). However, they are usually more inland and away from the warming influence of the ocean. As a result, it is a continental climate. This climate has seasonal temperatures – with warm summers and cold winters.
Df (continental): Continental climates have a seasonal temperature pattern. Moderate rainfall is present throughout the year.
Ds (subarctic): This climate also has seasonal temperature pattern. However rainfall is seasonal with a wet and dry season.
Polar (E) Climates
Polar climates are found in the highest latitudes (about 60°- 90° latitude). These are climates with very cold temperatures throughout the year.
EF (ice cap): Temperatures are below freezing year round. Very low rainfall is found throughout the year.
ET (tundra): Seasonal freezing and thawing temperatures occur throughout the year. Low rainfall is year round.
Reflections
Vocabulary
- climate
- precipitation
- temperature
Notes
- The Koppen climate classification system is based on temperature and precipitation.
- There are five basic types of climates (tropical, arid, temperate, cold and polar).
- Climate is the average weather conditions during a year for a particular location.
Bibliography
- An Atmosphere Study Guide
- About the Atmosphere
- Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification, Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., and McMahon, T. A. (University of Melbourne), Hydrology and Earth System Sciences.