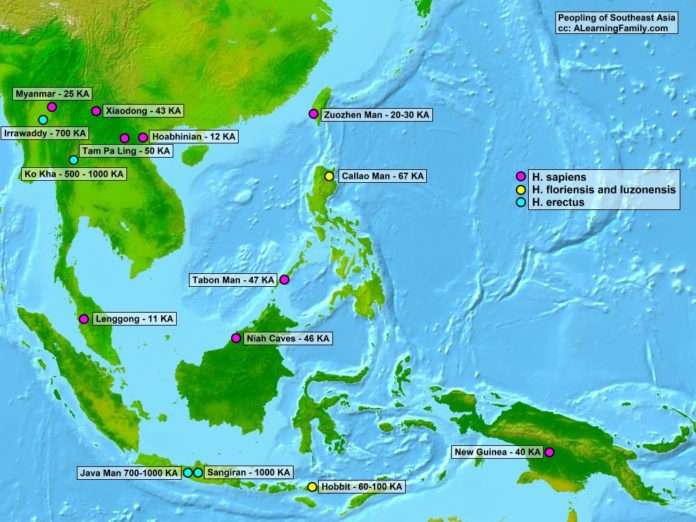
The human prehistory of Southeast Asia is based on fossil, linguistic, DNA, and other types of evidence. The history is quite complex because the evidence is not always clear cut. Continued research frequently brings about alternative and new understandings of this region.
What seems to be clear is that there were several waves of humans and pre-humans migrating into and within Southeast Asia. These waves shaped the peopling of Southeast Asia.
Prehistoric Human Ancestors
Java Man: Homo erectus
The first fossil evidence of Homo erectus was discovered in Indonesia in the 1890’s. This fossil was named the “Java man”. Java man existed between 0.7 and 1 million years ago. At that time, it lead to the hypothesis that modern man evolved in Asia. The discovery of another H. erectus in China (Peking man) in the 1920’s further supported this hypothesis.
However, in the 1960’s fossil remains of H. erectus were found in Africa. These remains were 1.4 to 1.9 million years old. These findings offered a different hypothesis. H. erectus and H. sapiens (modern humans) evolved in Africa and then migrated out of Africa to Asia.
At the present, the research indicates that H. erectus migrated to Myanmar and Thailand about 0.7 million years ago. Later, it entered Indonesia about 0.7 to 1 million years ago.
Callao Man and the Hobbit: H. luzonensis and H. floriensis
Other interesting fossil finds in Southeast Asia are the Callao Man and the Hobbit. Callao Man (H. luzonensis) is dated to about 67 thousand years ago. The fossil evidence was discovered in the Callao Caves in the Philippines. The Hobbit (H. floriensis) is about 60-100 thousand years old and was found in Indonesia.
Both fossil finds indicate that early forms of humans migrated into Southeast Asia. These findings could renew the hypothesis that modern humans evolved in Asia. However, the evidence is still being examined and these fossils could actually belong to H. sapiens.
Modern Humans in Southeast Asia
Homo sapiens sapiens
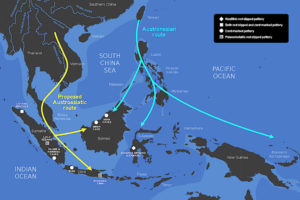
The story of modern humans (H. sapiens) in Southeast Asia is also complex and subject to debate. The archaeological record shows modern humans on mainland Asia dating from 11 to 50 thousand years ago. Evidence can be found in Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Laos, Vietnam, and China.
In maritime Southeast Asia, evidence can be found in the Philippines, Malaysia, and New Guinea. This evidence ranges from 40 to 50 thousand years ago. If Callao Man or the Hobbit turn out to be H. sapiens, this would be pushed back to 60 to 100 thousand years ago
Reflections
Vocabulary
- hypothesis
- migration
- peopling
Notes
- H. erectus probably migrated out of Africa and into Southeast Asia 0.7 million years ago.
- The earliest H. sapiens remains in Southeast Asia are about 67 thousand years old.
- Although debated, it is likely that H. sapiens also migrated out of Africa.