1Overview
The Lithosphere Study Guide provides a more organized approach to studying the lithosphere. It organizes articles into groups to guide you through the articles. Some students will find this approach useful in learning. The following article provides an overview of the lithosphere.
Recommended Reading
About the Surface of the Earth: An overview of the lithosphere.
2The Earth and the Sun
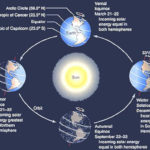
The relationship between the Earth and the sun affects our sense of time. This relationship is the cause of days and nights. It also creates the seasons.
Recommended Readings
Rotation of the Earth: Day and Night: Explores the Earth’s relationship with the sun that causes days and nights.
Revolution of the Earth: Year and Seasons: A review of the Earth’s relationship with the sun that causes the seasons.
3Structure of the Earth
The Earth is not uniform. Instead, it has three main layers like an onion. This is explored in the following article.
Recommended Reading
Structure of the Earth: Examines the structure of the Earth from the crust to the core.
4First Order Landforms
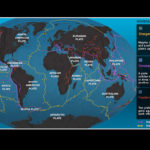
The Earth’s crust is not solid. Instead, it is broken up into many tectonic plates. These are the largest of the landforms.
Recommended Readings
Tectonic Plates: A Cracked Eggshell: An introduction to tectonic plates and their role in creating landforms.
First Order Landforms: Continents and Ocean Basins: A review of the Earth’s continents and ocean basins – the largest landforms.
5Second Order Landforms
Second order landforms are the result of tectonic plate movements. These are the largest landforms on the continents and ocean basins. These landforms are created at the boundaries of tectonic plates.
Recommended Readings
Andes: Collision of Oceanic and Continental Plates: Explores how the collision of an oceanic plate with a continental plate created the Andes.
Himalayas: Collision of Continental Plates: Explores how the collision of two continental plates created the Himalayas.
MidAtlantic Ridge: Divergence of Oceanic Plates: Creation of oceanic ridges from plate divergence.
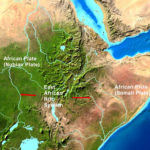
Great Rift Valley: Divergence of Continental Plates: Creation of continental rift valleys from plate divergence.
6Third Order Landforms
Third order landforms are smaller local landforms. They may be tectonic landforms that are being created. On the other hand, they may be erosional landforms created by erosional forces such as running water.
Recommended Readings
Hill: Chocolate Hills and Karst Landscapes: The formation of hills is explored.
Plain: A Flat but Varied Landform: How plains are created by deposition and erosion.
Plateau: Flat and Elevated: About plateaus and how they are created.
Shield Volcano: Quiet and Laid Back: A look at shield volcanoes and their origin.
Stratovolcano: Most Violent Eruptions: Explanation of what a stratovolcano is and how it is created.
Valley: Water and Ice Eroding the Earth: Examines the valley as a fluvial and glacial landform.