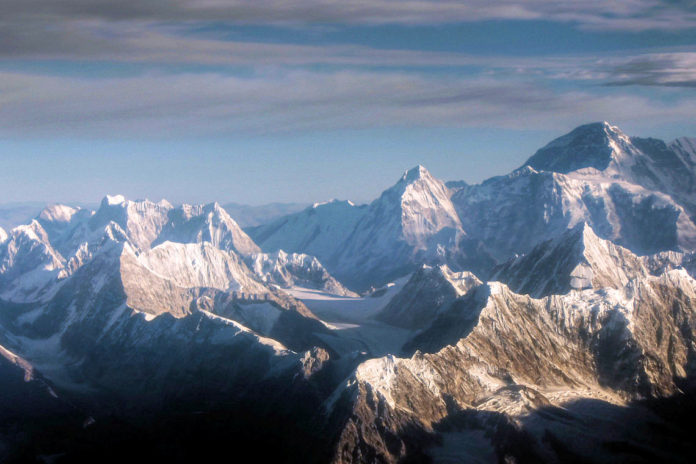
The Himalayas is a mountain range in northern India. A collision between the Indian and the Eurasian plates created the range. The mountain range is about 2,400 kilometers long. Mount Everest is located in this range. Everest is the highest peak in the world. However, there are fifty other peaks that are also among the highest in the world.
Origin of the Himalayas
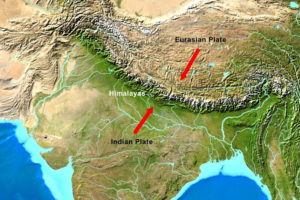
The Indian plate was part of the supercontinent Gondwana. However, it broke apart about 100 million years ago. The plate moved north and collided with the Eurasian plate 55 million years ago. This event started the creation of the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau.
Both of the continental tectonic plates have similar densities. Therefore, subduction did not occur. Instead, the collision caused folding and faulting. In turn, that produced uplift. And, that uplift lead to formation of mountain ranges and plateaus.
Importance of the Himalayas
Climate
Monsoon: The region’s climate changed when the range was created. The mountains produced a monsoon climate. The monsoon is a seasonal reversal of winds over southern Asia. This reversal brings rains during summer months and a dry season during winter.
Barrier: However, the mountain range also has a moderating influence. The mountains block cold continental air from flowing into South Asia. This results in a milder South Asian climate. When the monsoon winds blows inland, the mountain range brings rains to South Asia. However, this produces a dry climate north of the mountains. As a result, regions north of the mountains have desert climates. This resulted in a dry Tibetan plateau and the Gobi Desert.
People and Economy
Over 50 million people live within the Himalayas. However, nearly 600 million people live in the drainage basins south of the Himalayas. The rivers (Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra) flow south and provide a source of water and fertile agricultural soils. This is essential for agricultural production. In addition, the rivers provide a transportation network for the South Asian populations.
Reflections
Vocabulary
- drainage basin
- Gondwana
- monsoon
Notes
- The Himalayas are the result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- The mountain range is responsible for South Asia’s monsoon.
- The river systems that start in the mountains support over 600 million people.

