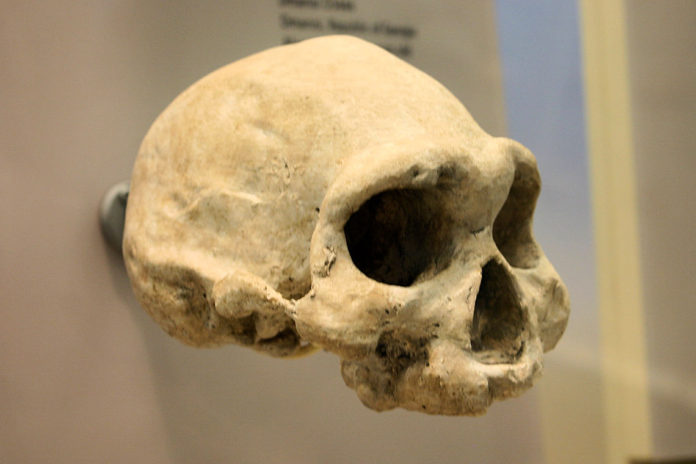
Homo erectus (upright man) lived between 1.9 and 0.25 million years ago. This early ancestor of humans developed a more human-like body. Unlike the apes, it had long legs and shorter arms. And, H. erectus was a biped almost as tall as modern humans.
Fossil evidence shows that H. erectus lived in Africa, West Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia. It may have also lived in Europe.
Characteristics of Homo erectus
What Makes Homo erectus Similar to Humans?
This ancestor of modern man made complex stone tools such as hand axes. These tools were probably used to hunt and skin animals. H. erectus was a hunter and gatherer. This means that it was an omnivore with a diet of meat and plants.
In addition, H. erectus could also use fire. Fire was used for cooking, keeping warm, and providing light. The use of fire began at least 400,000 years ago.
Etching on shells also indicate that H. erectus also practiced art. The primitive artwork dates to 430,000 years ago.
Physically, Homo erectus‘ fossil remains indicate that it walked upright on two feet. It had opposable thumbs for grasping tools. H. erectus was up to 1.8 meters tall and weighed up to 68 kilograms. However, it had a smaller brain, a thicker skull, no chin, and a pronounced brow ridge over its eyes.
Where Did H. erectus Live?
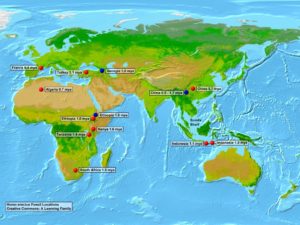
The oldest H. erectus fossil evidence comes from Kenya in East Africa. The fossil has been dated from 1.9-1.8 million years ago. Other old fossils have been found in Georgia (1.8 mya) and China (1.7 mya). This suggests that Homo erectus first evolved in Africa. It then migrated out of Africa to Asia.
The first fossil (Java man) was found in Indonesia in the 1890’s. In the 1920’s, another specimen was discovered in China (Peking man). This supported the hypothesis that modern man (H. sapiens) evolved in Asia.
However, the oldest H. erectus and H. sapiens fossils were later discovered in Africa. This supported the alternate hypothesis that H. erectus first evolved in Africa and later migrated to Asia.
Other forms of evidence such as stone tools suggest that H. erectus may have also migrated into Europe (e.g. France, Italy and the United Kingdom). However, the evidence is not conclusive at this point in time.
How and Why did H. erectus Migrate?
The most likely reason for the migration of H. erectus is environmental change. For example, climate changes may have provided a greater range of food sources in Asia. As a hunter and gatherer, H. erectus simply followed the food.
The Ice Ages also caused a lowering of the sea level. This created land bridges from mainland Asia to maritime Southeast Asia. Java Man probably entered Indonesia from mainland Asia over a land bridge.
Reflections
Vocabulary
- Homo erectus
- land bridge
- maritime Southeast Asia
Notes
- Homo erectus lived from 250,000 to 2 million years ago.
- H. erectus first evolved in Africa and later migrated out of Africa.
- This human ancestor was a hunter and gatherer who made sophisticated stone tools and used fire.