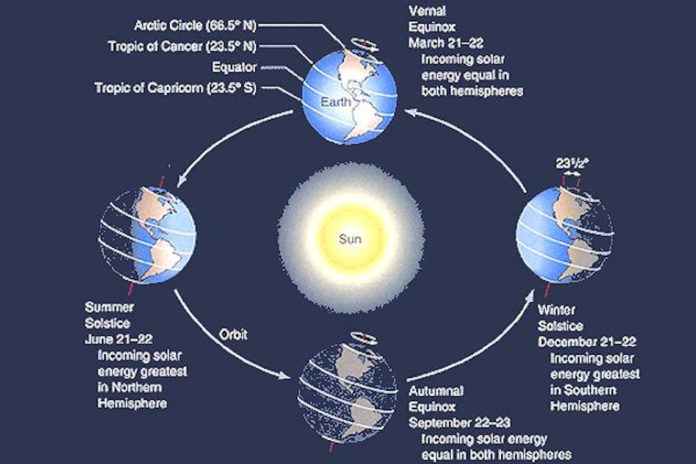
The revolution of the Earth is the movement of the Earth around the sun. The Earth takes 365¼ days to make one complete trip around the sun. This movement of the Earth around the sun creates the seasons and our year.
The Revolution of the Earth
The Year
The time it takes the Earth to make one revolution around the sun is a year. One solar year is 365¼ days. However, a calendar year is only 365 days long. Thus, every four years an extra day is created. This results in a leap year that is 366 days long. The extra day is added to February. During a regular year, February is 28 days long. However, during the leap year February is 29 days long. This extra day is an adjustment for the extra ¼ of a day in the solar year.
Earth’s Inclination
A line drawn from the North Pole to the South Pole through the center of the earth is its axis. However, the Earth’s axis is not straight up and down. The earth tilts by 23½ degrees. This tilt is the Earth’s inclination.
When combined with the Earth’s revolution, this inclination produces the seasons on the Earth.
Earth’s Seasons
As the Earth travels around the sun, the North Pole tilts toward the sun part of the year. When this happens, the Northern hemisphere experiences summer. The Northern hemisphere receives the most sunlight because it has longer days and stronger sunlight.
However, for part of the year, the North Pole tilts away from the sun. During this time, the Northern hemisphere experiences winter. The Northern hemisphere now receives the least sunlight due to shorter days and weaker sunlight.
The seasons are reversed in the Southern hemisphere.
Reflections
Vocabulary
- inclination
- revolution
- seasons
Notes
- The earth revolves around the sun every 365¼ days.
- The length of time for one revolution is what we call a year.
- The earth’s inclination and revolution creates the seasons.