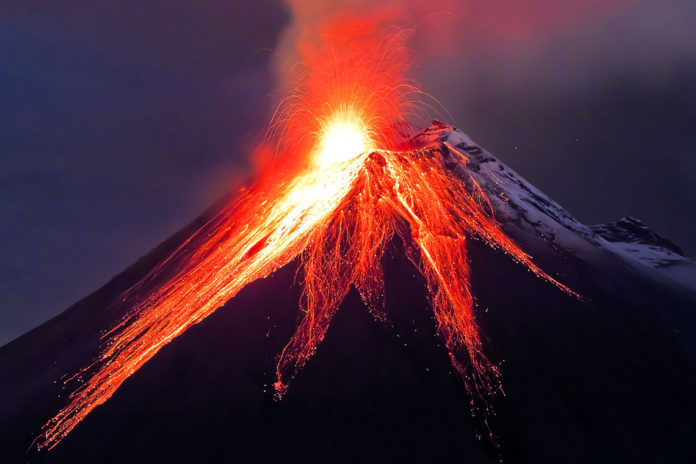
A stratovolcano is a large cone shaped volcano. It is found near subduction zones. Subduction zones occur where tectonic plates collide. Stratovolcanoes are known as composite volcanoes. These landforms are a composite of layers of lava, ash, and other materials.
What is a Composite Volcano?
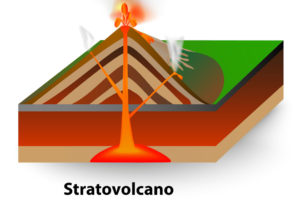
Over a period of time, the stratovolcano experiences different types of eruptions. Gentle lava flows may dominate for a while. These flows build up the volcano with sheets of lava.
The lava flows will alternate with explosive eruptions. These eruptions produce clouds of ash that build up layers of ash or pumice. In this manner, the volcano becomes a composite of layers of different materials.
What is the Danger of a Stratovolcano?
Stratovolcanoes pose many dangers. Some are far more dangerous than others. The major dangers are:
Pyroclastic flows: A pyroclastic flow is a rapidly moving cloud of hot gases and rocks. Temperatures can be as high as 1000°C. The hot cloud can move as fast as 700 kilometers per hour. In 79 AD, pyroclastic flows from Mt. Vesuvius killed up to 25,000 people.
Volcanic bombs: Chunks of lava thrown from a volcano are bombs. The size of the bombs can range from a few centimeters to over five meters.
Volcanic ash: Stratovolcano eruptions produce large clouds of volcanic ash. Ash are very fine particles. The ash may cover surrounding areas and damage buildings and farms. If caught in a cloud of ash, the dust can be a danger to human health when inhaled. In the sky, the ash poses a danger to aircraft. Over a period of time, the ash may even have an effect on the earth’s climate by blocking sunlight.
Lava flows: Lava is molten rock at the Earth’s surface. It is much slower moving than a pyroclastic flow, but can cause considerable damage to areas with human settlements.
Mt. Pinatubo Eruption
Mount Pinatubo is a stratovolcano on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. It was inactive for over 500 years. However, in 1991 it erupted violently. It was the second largest eruption in the 20th century.
About 900 people died. The effects of the eruption also affected the lives of millions of people. More than 80,000 homes were damaged. Forests and farms were destroyed by pyroclastic flows or ash falls. Large clouds of ash caused a cooling of the northern hemisphere. The clouds also included sulfur dioxide which produced sulfuric acid droplets in the atmosphere.
Reflections
Vocabulary
- lava
- pyroclastic flow
- stratovolcano
Notes
- A stratovolcano is an explosive landform. It occurs near subduction zones.
- The cone-shaped volcano has alternating layers of lava and ash.
- Hazards from stratovolcanoes can be immediate and local or long term and global.

